When elevating your gaming experience, the right CPU can make all the difference. In this guide, we’ve curated a list of the best gaming CPUs you can buy right now, tailored to suit various needs and budgets. Let’s explore the cutting-edge technology that will help you boost your gameplay and dominate the competition.

CPU (Central Processing Unit)
The primary component of a computer that performs most of the processing tasks. It’s often referred to as the “brain” of the computer. The CPU executes instructions from programs by performing basic arithmetic, logic, control, and input/output operations.
Key Factors to Consider for the Best Gaming CPU
Core Count

Core count is the number of independent processing units (cores) within a CPU. Each core can execute tasks independently, allowing the CPU to handle multiple processes simultaneously.
Modern CPUs typically have multiple cores, enabling better multitasking and parallel processing. For example, a quad-core CPU has four processing units, each capable of running separate instructions.
Recommended Core Counts for Best Gaming CPU
| Use Case | Core Count | Examples |
|---|---|---|
| Casual Gaming (Older Titles) | 4 Cores | Intel Core i3-12100, AMD Ryzen 3 5300G |
| Mainstream Gaming (Modern Titles) | 6-8 Cores | Intel Core i5-13600K, AMD Ryzen 5 7600X |
| High-End Gaming/Streaming | 8-12 Cores | Intel Core i7-13700K, AMD Ryzen 7 7800X3D |
| Professional Gaming/Content Creation | 12-16+ Cores | Intel Core i9-13900K, AMD Ryzen 9 7950X |
Key Brands

Popular Intel CPUs for Gaming
| Processor | Cores/Threads | Best For |
|---|---|---|
| Intel Core i3-12100F | 4/8 | Entry-level gaming. |
| Intel Core i5-13600K | 14/20 | Best value for gaming. |
| Intel Core i7-13700K | 16/24 | High-end gaming/streaming. |
| Intel Core i9-13900K | 24/32 | Enthusiasts and multitasking. |
AMD is renowned for offering excellent performance per dollar and strong multi-threaded capabilities.
Popular AMD CPUs for Gaming
| Processor | Cores/Threads | Best For |
| AMD Ryzen 5 5600 | 6/12 | Budget gaming. |
| AMD Ryzen 5 7600X | 6/12 | Mid-range gaming. |
| AMD Ryzen 7 7800X3D | 8/16 | High-performance gaming. |
| AMD Ryzen 9 7950X | 16/32 | Enthusiasts and creators. |
Intel vs AMD: Which Brand Offers the Best Gaming CPU?
| Factor | Intel | AMD |
|---|---|---|
| Single-Core Performance | Stronger in gaming, higher clock speeds. | Excellent, but slightly behind Intel. |
| Multi-Core Performance | Good for gaming + light multitasking. | Better for multitasking and streaming. |
| Price-to-Performance | Slightly higher prices for premium CPUs. | More affordable options for similar performance. |
| Integrated Graphics | Widely available, basic gaming possible. | Limited to “G” series (better graphics). |
| Overclocking | Limited to “K” series models. | Unlocked across the lineup. |
Threads

A thread in a CPU represents a sequence of instructions that a processor can handle independently. Modern CPUs often feature technologies like Simultaneous Multi-Threading (SMT) (AMD) or Hyper-Threading (HT) (Intel) to create virtual threads, effectively doubling the number of threads per core.
How Many Threads Are Needed for Best Gaming CPUs?
| Gaming Scenario | Recommended Thread Count | Example CPUs |
|---|---|---|
| Casual gaming (light tasks) | 8 Threads | Intel Core i3-12100, AMD Ryzen 5 5600 |
| Mainstream gaming (modern titles) | 12 Threads | Intel Core i5-13600K, AMD Ryzen 5 7600X |
| Gaming + streaming | 16 Threads | Intel Core i7-13700K, AMD Ryzen 7 7800X3D |
| High-end gaming/content creation | 24+ Threads | Intel Core i9-13900K, AMD Ryzen 9 7950X |
Why Are Threads Important for Gaming?
Improved Multitasking
Games don’t operate in isolation. Background tasks like voice chat apps, game launchers, and streaming software compete for CPU resources. CPUs with more threads handle these additional tasks without compromising game performance.
Enhanced Game Performance
Modern games are designed to utilize multiple threads, distributing workloads across the CPU. Threads ensure smoother gameplay by handling physics calculations, AI processes, and rendering tasks simultaneously.
Example: Games like Cyberpunk 2077 or Battlefield 2042 benefit from CPUs with higher thread counts.
Future-Proofing Your PC
As gaming engines evolve, more games are being optimized for multi-threaded performance. A CPU with a higher thread count ensures longevity, allowing you to play upcoming titles without upgrading.
Better Streaming and Recording
If you’re gaming and streaming on platforms like Twitch, additional threads are essential. CPUs with higher thread counts can handle game rendering and video encoding simultaneously, delivering lag-free streams.
Best Gaming CPUs with High Thread Counts

Threads:20| Ideal for: Mainstream gamers looking for value and multitasking.
Threads:16| Ideal for: High-end gaming with optimized cache performance.
Threads: 32| Ideal for: Professional gamers and streamers.
Threads: 32|Ideal for: Gaming, streaming, and content creation.
Tip!
A higher thread count improves multitasking and performance in multi-threaded games but works best when paired with sufficient physical cores.
Clock Speed

Clock speed, measured in gigahertz (GHz), indicates how many cycles a CPU can complete per second.
Importance of Clock Speed in Gaming
Improved Single-Threaded Performance
Many games rely heavily on single-threaded performance, where a higher clock speed ensures faster execution of game logic, AI, and physics calculations. Games like CS and The Witcher 3 benefit significantly from CPUs with high clock speeds.
Smoother Gameplay
Higher clock speeds reduce latency and improve frame rates, especially in CPU-bound games. For competitive, best gaming, a CPU with a high clock speed ensures minimal lag and faster responses.
Better GPU Utilization
Modern GPUs rely on the CPU to feed them data. A CPU with a higher clock speed can prevent bottlenecks, allowing the GPU to perform at its maximum potential.
Enhanced Multitasking
Gaming often involves multitasking (e.g., running Discord, streaming software, or background applications). A higher clock speed ensures these tasks don’t interrupt your gaming performance.
How Much Clock Speed Do You Need for Gaming?
| Gaming Scenario | Recommended Clock Speed | Example CPUs |
|---|---|---|
| Casual gaming (light titles) | 3.5 – 4.0 GHz | Intel Core i3-12100, AMD Ryzen 5 5600 |
| Mainstream gaming (modern titles) | 4.0 – 4.5 GHz | Intel Core i5-13600K, AMD Ryzen 5 7600X |
| High-end gaming | 4.5 GHz and above | Intel Core i7-13700K, AMD Ryzen 7 7800X3D |
| Competitive/Esports gaming | 4.8 GHz and above | Intel Core i9-13900K, AMD Ryzen 9 7950X |
Clock Speed vs. Core Count

While clock speed determines how fast a CPU executes tasks, core count indicates how many tasks the CPU can handle simultaneously. For gaming:
- Single-core dependent games: Prioritize higher clock speed.
- Modern multi-threaded games: Balance clock speed with sufficient cores (6-8 cores for most games).
Best Gaming CPUs with High Clock Speeds
| Processor | Base Clock | Boost Clock | Best For |
|---|---|---|---|
| Intel Core i5-13600K | 3.5 GHz | 5.1 GHz | Mainstream gaming builds. |
| AMD Ryzen 5 7600X | 4.7 GHz | 5.3 GHz | High clock speed on a budget. |
| Intel Core i7-13700K | 3.4 GHz | 5.4 GHz | High-end gaming. |
| AMD Ryzen 7 7800X3D | 4.2 GHz | 5.0 GHz | Gaming with 3D V-Cache. |
Cache
Cache is a small amount of high-speed memory built directly into the CPU. It stores frequently accessed data and instructions, allowing the processor to retrieve them faster than it would from the main system RAM. Cache significantly reduces latency, improving the overall speed and efficiency of the CPU.
Types of Cache:
- L1 Cache (Level 1)
- The smallest and fastest type of cache.
- Stores critical data for immediate access.
- L2 Cache (Level 2)
- Larger but slightly slower than L1 cache.
- Handles more data and complements L1 cache.
- L3 Cache (Level 3)
- Largest and slower compared to L1 and L2.
- Shared across all CPU cores and is essential for gaming performance.
Importance of Cache in Gaming
- Faster Data Access
- Cache reduces the time the CPU spends fetching data from RAM.
- Quick access to game-related data, such as textures, physics, and AI calculations, ensures smoother gameplay.
- Improved Frame Rates
- High L3 cache size directly influences frame rates in CPU-intensive games like Total War and Flight Simulator.
- CPUs with technologies like AMD’s 3D V-Cache significantly boost gaming performance.
- Reduced Latency
- Cache minimizes latency by keeping frequently used data close to the CPU cores.
- This is particularly crucial for real-time games like Battlefield or Fortnite, where milliseconds matter.
- Better Multi-Core Performance
- Shared L3 cache enhances communication between cores.
- Multi-threaded games, which distribute workloads across multiple cores, benefit greatly from larger caches.
- Enhanced Streaming and Multitasking
- Games running alongside tasks like streaming or video recording rely heavily on cache for efficient multitasking.
- More cache ensures these tasks don’t hinder gaming performance.
How Much Cache Do You Need for Gaming?
The cache size needed depends on your gaming and multitasking requirements:
| Gaming Scenario | Recommended L3 Cache | Example CPUs |
|---|---|---|
| Casual gaming (light titles) | 12MB – 16MB | Intel Core i3-12100, AMD Ryzen 5 5600 |
| Mainstream gaming (modern titles) | 20MB – 30MB | Intel Core i5-13600K, AMD Ryzen 5 7600X |
| High-end gaming | 32MB – 64MB | Intel Core i7-13700K, AMD Ryzen 7 7800X3D |
| Competitive/Esports gaming | 64MB and above | AMD Ryzen 9 7950X, Intel Core i9-13900K |
Cache in Modern CPUs
- AMD’s 3D V-Cache Technology
- AMD’s Ryzen 7000X3D series (e.g., Ryzen 7 7800X3D) comes with stacked L3 cache, significantly improving gaming performance.
- Ideal for CPU-bound games.
- Intel’s Smart Cache
- Intel CPUs use Smart Cache technology to dynamically allocate cache resources across cores for better gaming efficiency.
Best Gaming CPUs with High Cache
| Processor | L3 Cache | Best For |
|---|---|---|
| AMD Ryzen 7 7800X3D | 96MB | High-end gaming with CPU-bound titles. |
| Intel Core i5-13600K | 24MB | Mainstream gaming performance. |
| AMD Ryzen 9 7950X | 64MB | Gaming, streaming, and multitasking. |
| Intel Core i9-13900K | 36MB | Enthusiast-level gaming and content creation. |
CPU Socket
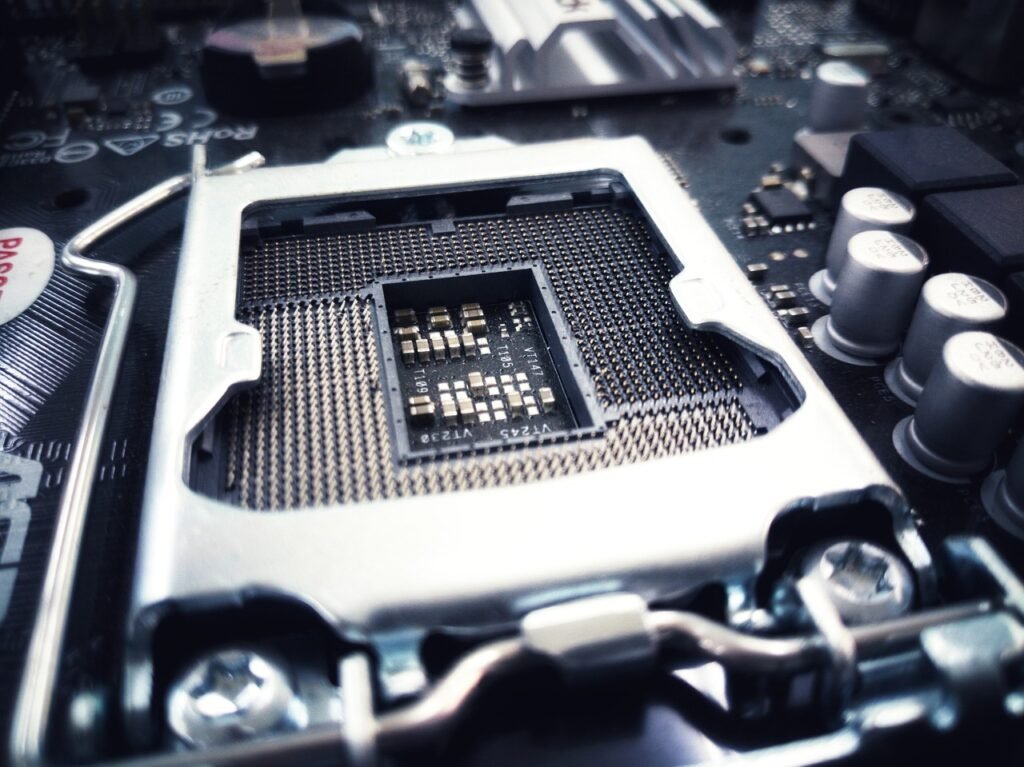
A CPU socket is the physical interface on the motherboard where the processor (CPU) is installed. It serves as the connection point between the CPU and the motherboard, allowing data to flow and ensuring power delivery.
Each CPU socket is designed to work with specific CPU models and manufacturers.
Types of CPU Sockets:
- PGA (Pin Grid Array):
- The CPU has pins that fit into holes in the socket.
- Common in older AMD processors (e.g., AM3, AM4).
- LGA (Land Grid Array):
- The socket has pins, and the CPU has flat contact points.
- Used in Intel CPUs and AMD’s newer AM5 socket.
- BGA (Ball Grid Array):
- Permanent soldered connection between CPU and motherboard.
- Common in laptops, not for gaming PCs.
Importance of a CPU Socket in Gaming
- Compatibility
- The CPU socket determines which processors are compatible with your motherboard.
- For example:
- Intel 13th Gen processors require an LGA 1700 socket.
- AMD Ryzen 7000 series uses the AM5 socket.
- Future Upgrade Potential
- Some sockets, like AMD’s AM4, support multiple generations of CPUs, offering better upgrade paths.
- Choosing a socket with a long lifespan ensures your gaming PC remains future-proof.
- Optimal Performance
- A compatible CPU and socket ensure stable connections and proper power delivery, critical for gaming performance.
- Incorrect socket-CPU combinations may lead to performance bottlenecks or system instability.
- Overclocking Support
- Certain sockets are optimized for overclocking, allowing users to push their CPU for better gaming performance.
- Example: Intel’s Z690 chipset (LGA 1700) and AMD’s X670 chipset (AM5) support overclocking.
- Gaming Features and Connectivity
- Modern sockets often support advanced features like PCIe 5.0, DDR5 RAM, and high-speed NVMe SSDs, all of which are important for gaming.
- Example: AMD AM5 and Intel LGA 1700 both support PCIe 5.0 and DDR5.
Popular CPU Sockets for Gaming
| Socket Type | Supported CPUs | Best For |
|---|---|---|
| LGA 1700 | Intel 12th and 13th Gen CPUs | High-performance gaming with Intel CPUs. |
| AM5 | AMD Ryzen 7000 series | Cutting-edge gaming and future-proofing. |
| AM4 | AMD Ryzen 1000 to 5000 series CPUs | Budget and mainstream gaming. |
How to Choose the Right Socket for Gaming?
- Identify the CPU You Need:
- Decide between Intel and AMD based on gaming performance and budget.
- Ensure the motherboard you select has the socket required for your chosen CPU.
- Check Compatibility with Features:
- Consider Future Upgrades:
- AMD’s AM5 socket is designed for multiple future CPU generations, while Intel’s LGA 1700 may be replaced after 13th Gen CPUs.
Top Best Gaming CPUs and Their Sockets
| Processor | Socket | Best For |
|---|---|---|
| Intel Core i5-13600K | LGA 1700 | Mainstream gaming. |
| AMD Ryzen 5 7600X | AM5 | High-performance gaming on a budget. |
| Intel Core i9-13900K | LGA 1700 | Enthusiast-level gaming and multitasking. |
| AMD Ryzen 7 7800X3D | AM5 | CPU-bound gaming with 3D V-Cache. |
Summary
Recommended Best Gaming CPUs with Key Features
| Processor | Cores/Threads | Clock Speed | Cache | Socket Type |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Intel Core i5-13600K | 14/20 | 3.5-5.1 GHz | 24MB L3 | LGA 1700 |
| AMD Ryzen 7 7800X3D | 8/16 | 4.2-5.0 GHz | 96MB L3 (3D) | AM5 |
| Intel Core i7-13700K | 16/24 | 3.4-5.4 GHz | 30MB L3 | LGA 1700 |
| AMD Ryzen 9 7950X | 16/32 | 4.5-5.7 GHz | 64MB L3 | AM5 |



